Understanding the key features and applications of insecticides is crucial for effective pest management. Below is a concise summary of 20 commonly used insecticides:
1、Emamectin Benzoate: Acts through stomach poisoning and contact. Causes irreversible paralysis in pests, leading to death within 2–4 days. Effective against Lepidoptera pests and thrips, with slow action but crop safety.
2、Imidacloprid: Offers contact, stomach, and systemic action. Causes pest paralysis and death with quick results. Most effective against piercing-sucking pests like aphids, especially at higher temperatures.
3、Thiamethoxam: A systemic neonicotinoid effective against thrips, aphids, and psyllids. Suitable for both root application and spraying.
4、Tebufenozide: Promotes molting in Lepidoptera larvae. Stops feeding within 6–8 hours and causes death in 3–4 days. Safe for crops, with no phytotoxicity.
5、Chlorbenzuron: Most effective when applied during the early larval stages. Ineffective on adults but safe for natural enemies. Best for Lepidoptera and fly larvae, with peak effects after 3–5 days.
6、Chlorantraniliprole: Long-lasting and low-toxicity. Highly effective against Lepidoptera pests, such as rice leaf rollers and stem borers.
7、Pymetrozine: Primarily targets rice planthoppers. Slow-acting and increasingly less effective due to resistance. Limited effectiveness against some aphids.
8、Nitenpyram: Effective for aphids and rice planthoppers. Quick action but short residual activity, with rising resistance issues.
9、Acetamiprid: Exhibits contact and stomach toxicity. Targets aphids, leafhoppers, whiteflies, and certain beetles. Less effective at lower temperatures.
10、Buprofezin: Controls scale insects effectively. Previously used for rice planthoppers, but resistance has reduced its usage. Avoid contact with cabbage and radish crops.
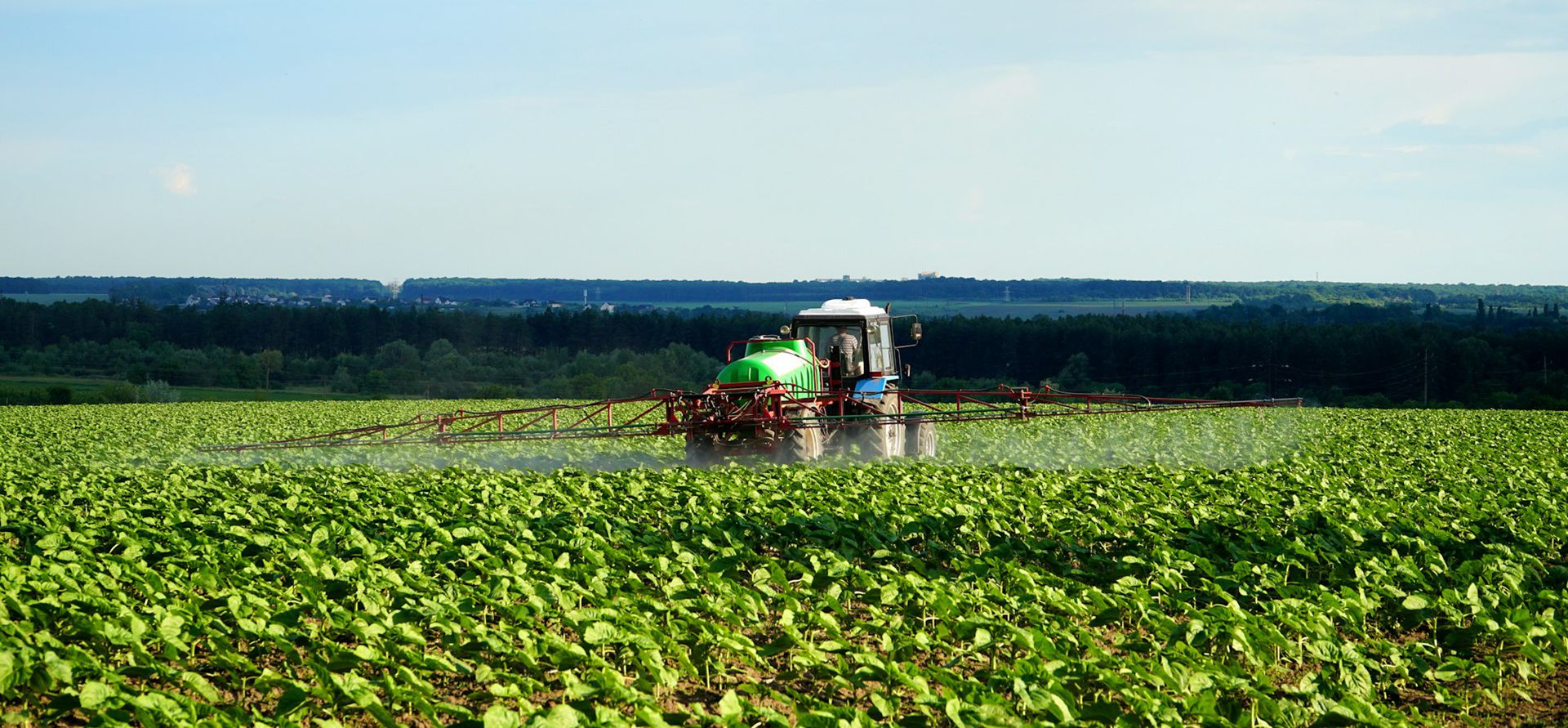

11、Isoprocarb: A contact insecticide with certain systemic properties. Fast-acting and effective against rice planthoppers, leafhoppers, and thrips.
12、Bifenthrin: Insecticide and acaricide with fast-acting stomach and contact toxicity. Suitable for Lepidoptera pests and mites.
13、Chlorpyrifos: Broad-spectrum insecticide with stomach, contact, and fumigation effects. Effective against underground pests, Lepidoptera, mites, and nematodes. Caution needed for cucurbit seedlings.
14、Deltamethrin: Offers contact, stomach toxicity, and repellence. Effective against Lepidoptera larvae but has weak penetration and is ineffective on mites.
15、Cyhalothrin: Highly toxic to both insects and mites, with strong contact and stomach action. May cause skin irritation in sensitive individuals.
16、Cyfluthrin: Effective for soil-dwelling pests through contact and stomach action.
17、Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt): A biological insecticide often combined with other ingredients to enhance efficacy.
18、Abamectin: A broad-spectrum antibiotic-based insecticide and acaricide. Effective against red spider mites, leaf rollers, and high doses for stem borers.
19、Metaldehyde: Molluscicide for snails and slugs. Effectiveness decreases in extreme temperatures (below 1.5°C or above 35°C).
20、Hexaflumuron: Insecticide with strong ovicidal activity. Fast-acting and effective against pests like cotton bollworms, leaf rollers, and stem borers.
This guide simplifies the technical details for better understanding and practical use of these insecticides. Effective application and resistance management are key to maximizing their benefits.